Sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) is a nontoxic, nonflammable and chemically stable gas that is widely used as an arc quenching medium in medium-voltage (MV) and high-voltage (HV) circuit breakers and as an insulating medium in gas-insulated substations (GIS) and gas-insulated lines (GIL). However, SF6 has been designated as one of the six greenhouse gases by the Kyoto Protocol because the global warming potential (GWP) of SF6 is nearly 24000 times higher than that of CO2 over a 100 year interval. Additionally, SF6 decomposes into lower fluorides of sulphur which in turn react with electrodes or gas impurities to form many toxic products, such as sulphur dioxide, hydrofluoric acid and metal fluoride compounds, which are hazardous to maintenance personnel. Finding suitable substitutes to SF6 is therefore an urgent task.
Electron Energy Distribution Function (EEDF)
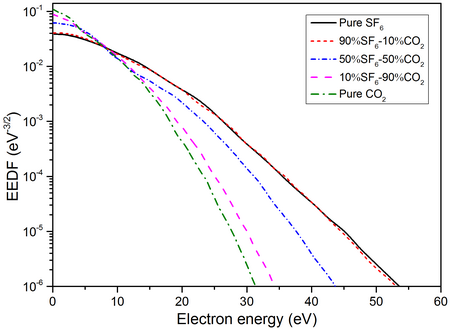
EEDF of different SF6-CO2 mixtures at a reduced electric field strength E/N of 200Td, a temperature of 2000K and a pressure of 0.1MPa.
Ionization Coefficients ($\alpha/N$)
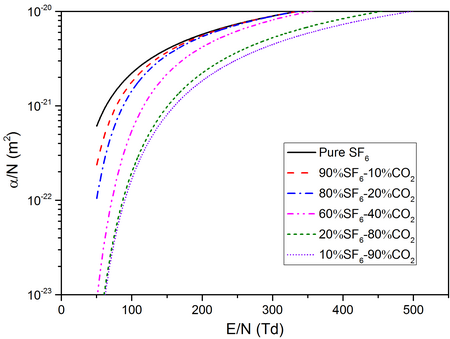
$\alpha/N$ of different SF6-CO2 mixtures as a function of $E/N$ at a temperature of 2000K and a pressure of 0.1MPa.
Electron Attachment Coefficients ($\eta/N$)
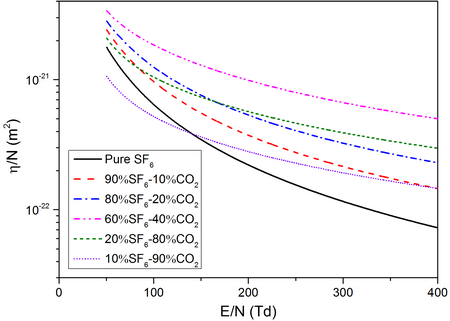
$\eta/N$ of different SF6-CO2 mixtures as a function of $E/N$ at a temperature of 2000K and a pressure of 0.1MPa.
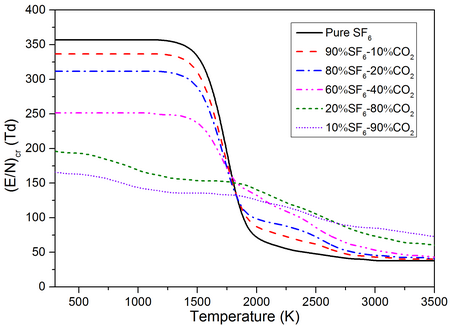
Critical Electric Field Strength ($(E/N)_{cr}$)