Plasma simulation is an important and sometimes only approach to investigating plasma behavior. We have proposed two general AI-driven frameworks for low-temperature plasma simulation: Coefficient-Subnet Physics-Informed Neural Network (CS-PINN) and Runge-Kutta Physics-Informed Neural Network (RK-PINN). CS-PINN uses either a neural network or an interpolation function (e.g. spline function) as the subnet to approximate solution-dependent coefficients (e.g. electron-impact cross sections, thermodynamic properties, transport coefficients, et al.) in plasma equations. On the basis of this, RK-PINN incorporates the implicit Runge-Kutta formalism in neural networks to achieve a large-time-step prediction of transient plasmas. Both CS-PINN and RK-PINN learn the complex non-linear relationship mapping from spatio-temporal space to equation’s solution.
AI-driven plasma simulation framework
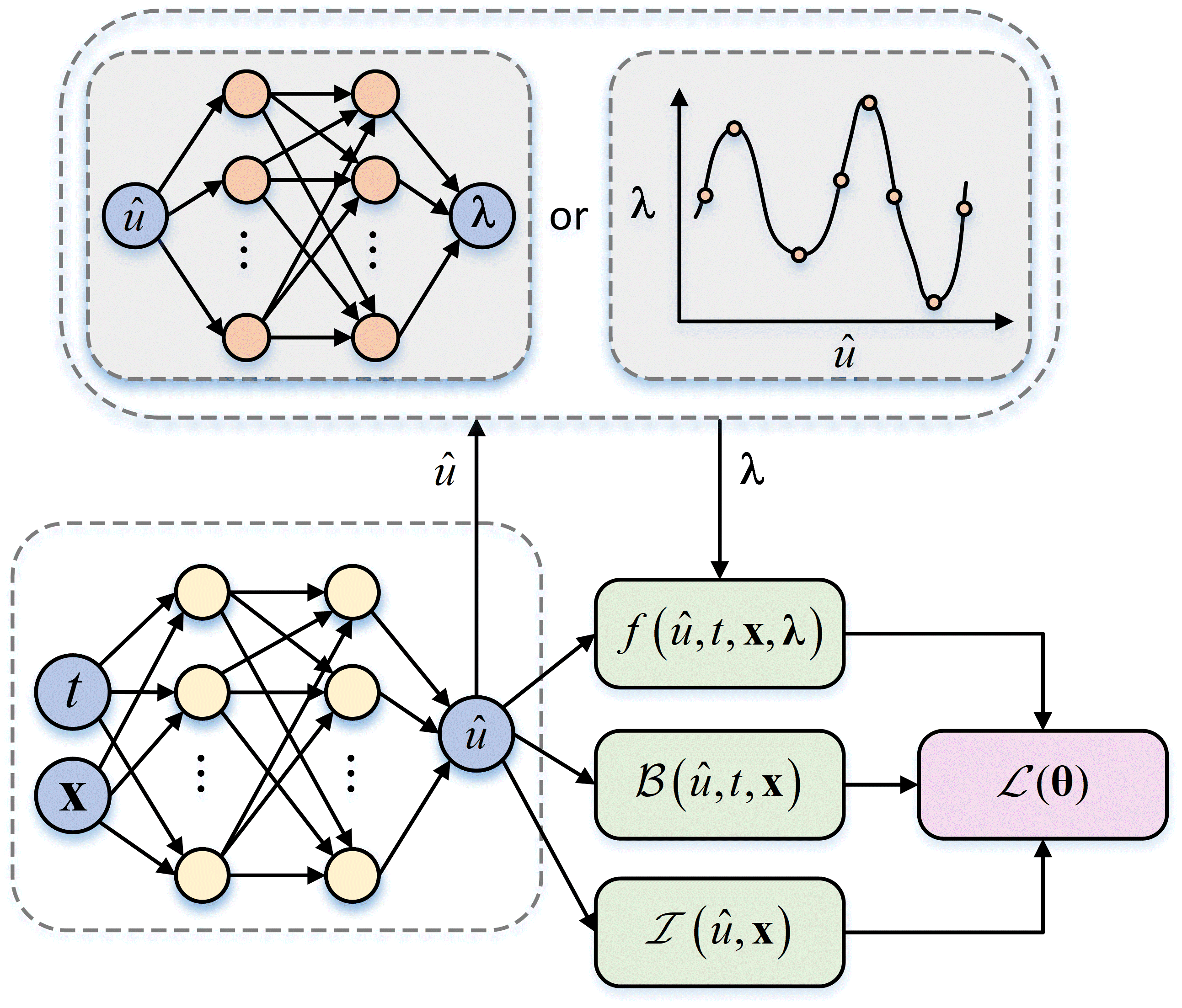
Coefficient-Subnet Physics Informed Neural Network (CS-PINN) for solving plasma equations with solution-dependent coefficients
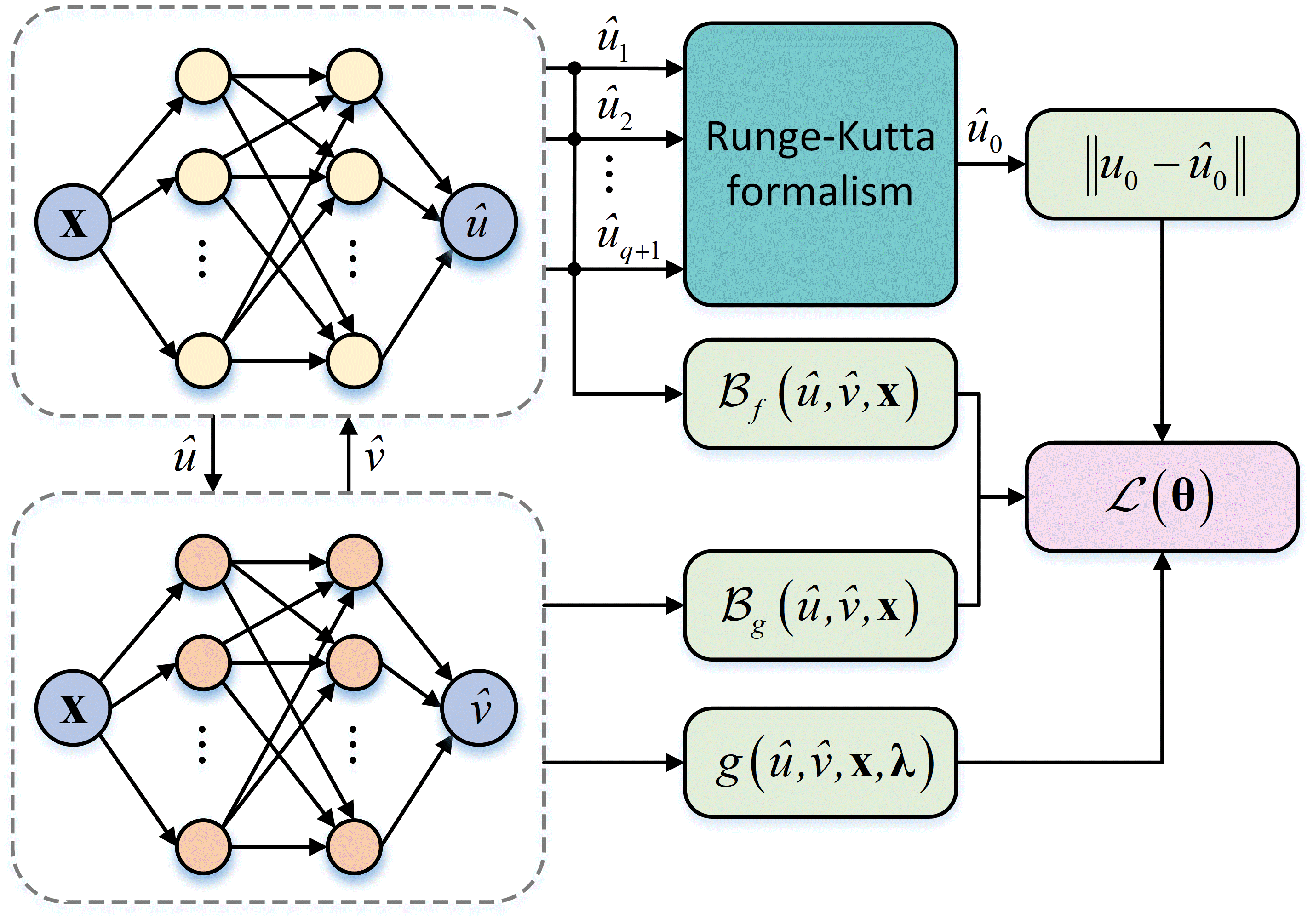
Runge-Kutta Physics Informed Neural Network (RK-PINN) for solving plasma equations with transient terms.
Case 1: Solving Boltzmann equation for electron transport in weakly ionized plasma
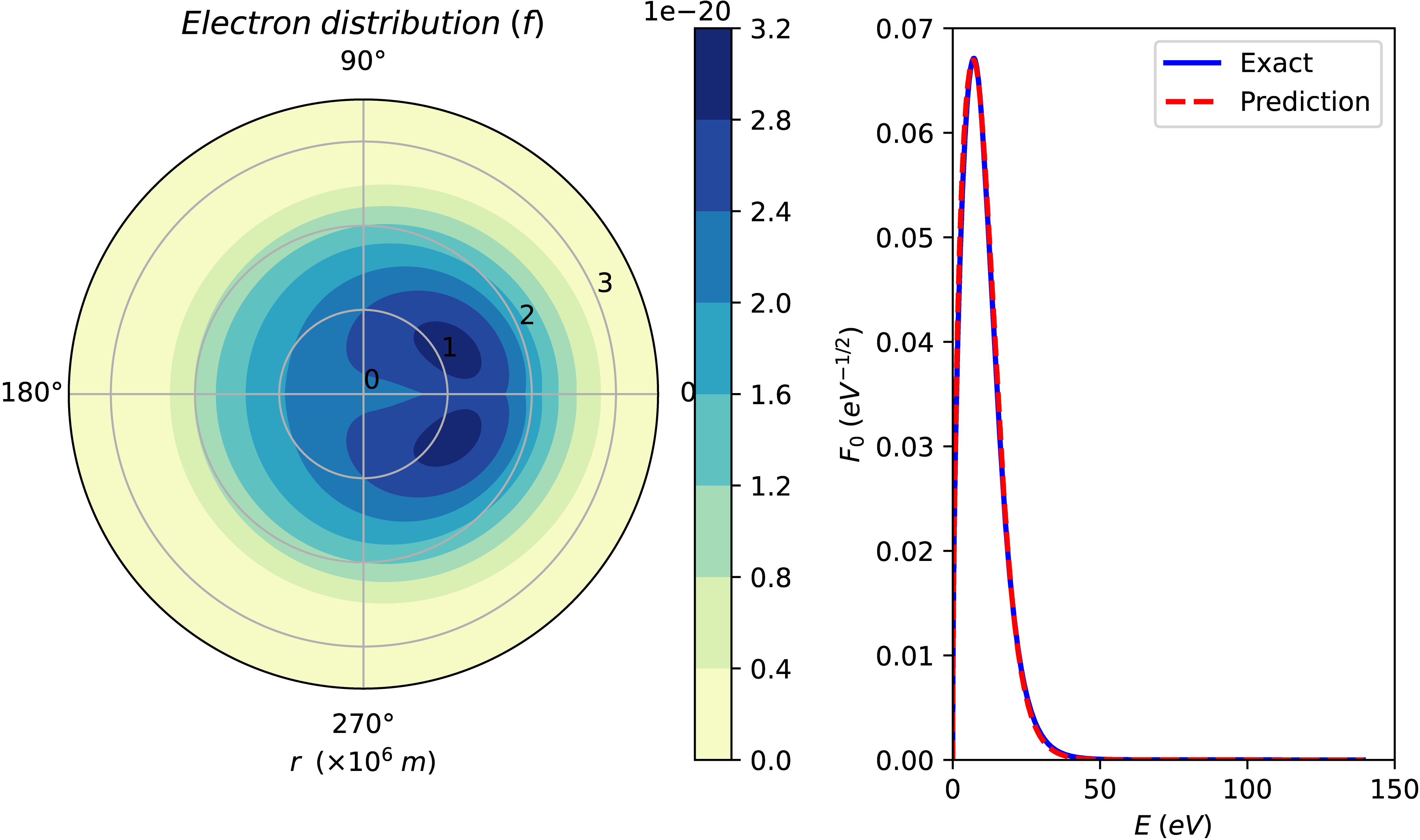
Electron distribution of argon plasma at E/N of 500 Td predicted by CS-PINN
Case 2: Solving drift-diffusion-Poisson equations for 1-D DC corona discharge plasma
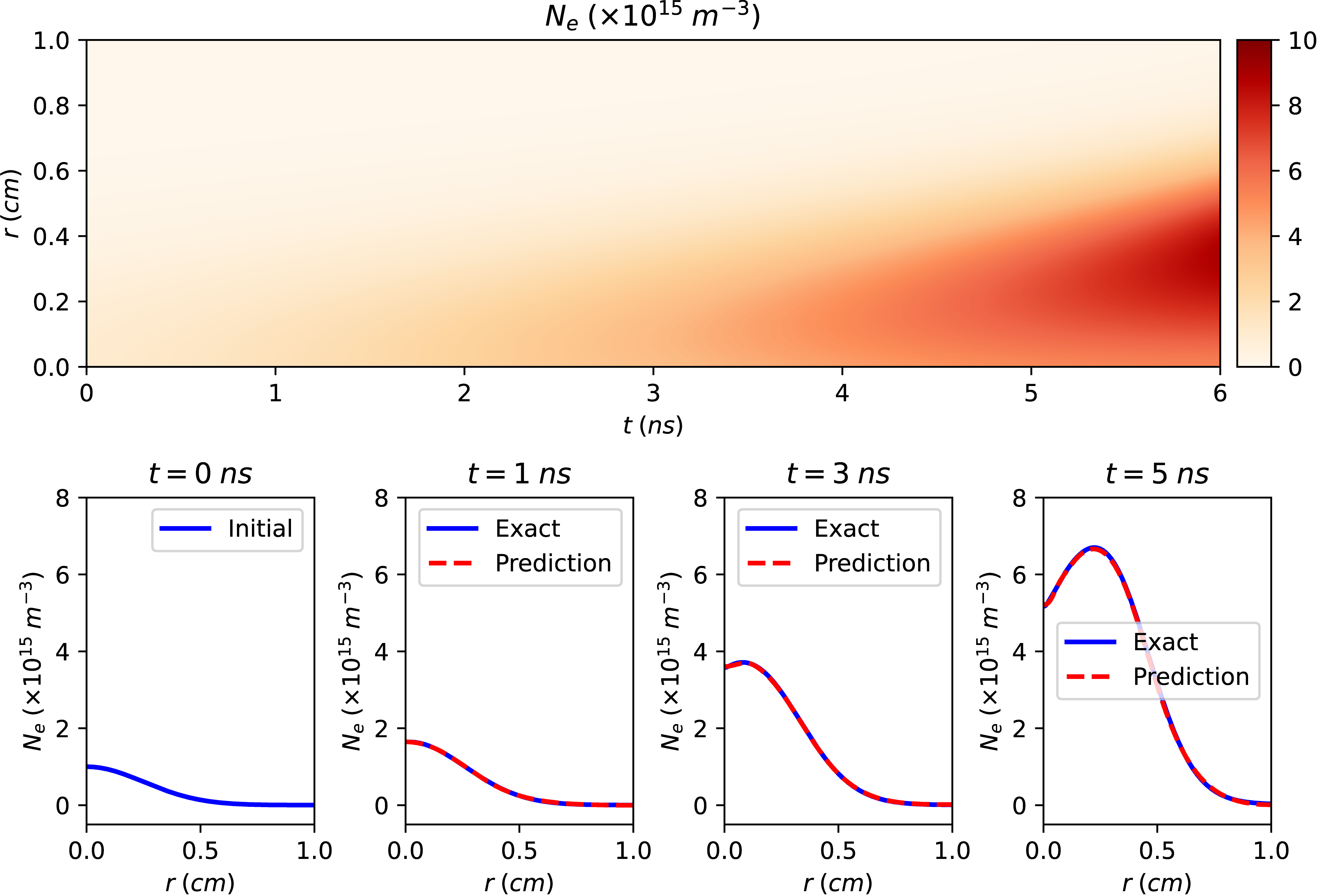
Number density of electrons predicted by RK-PINN
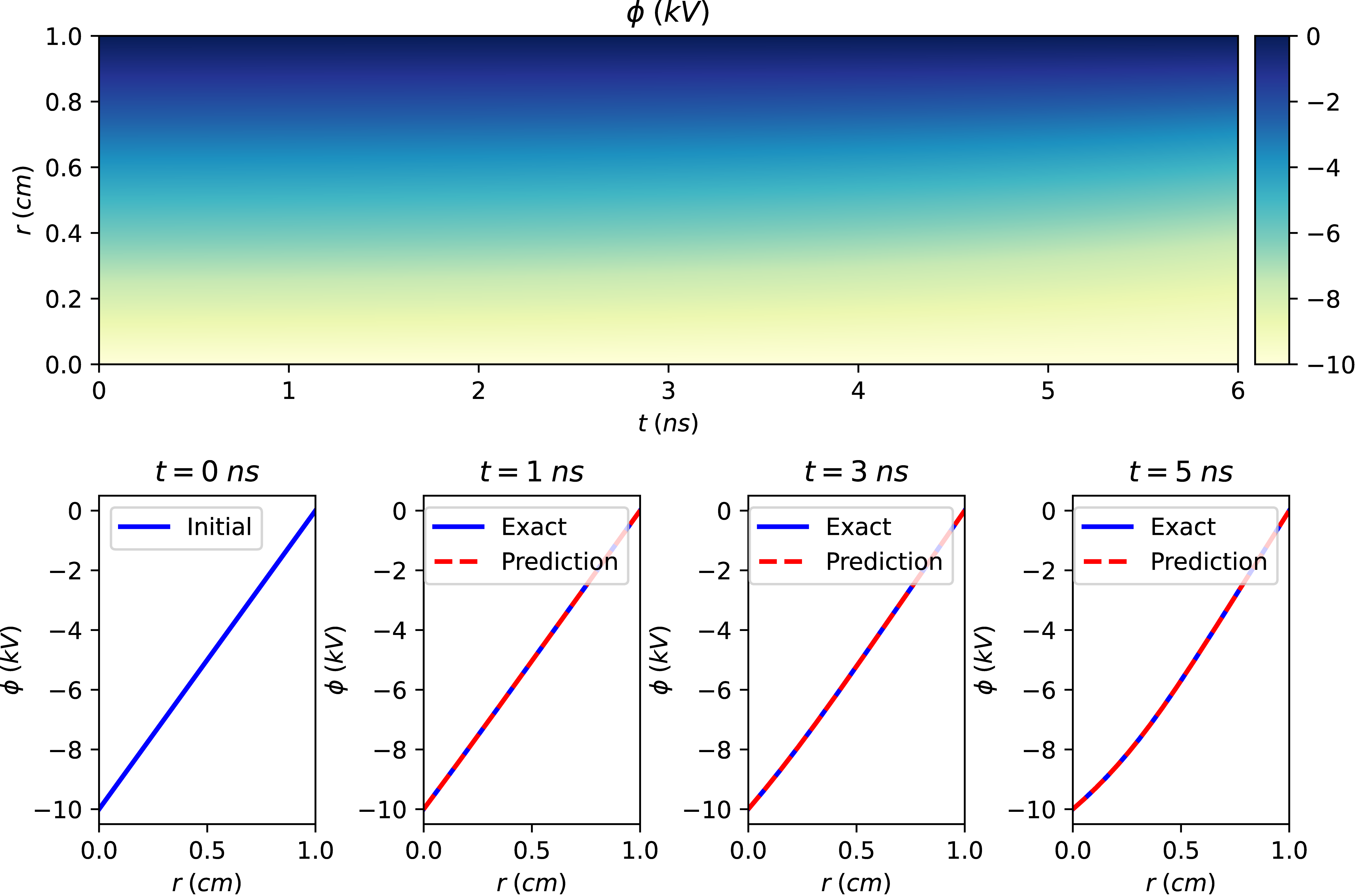
Electric potential predicted by RK-PINN
Case 3: Solving time-dependent Elenbaas-Heller equation for 1-D arc plasma with radial velocity
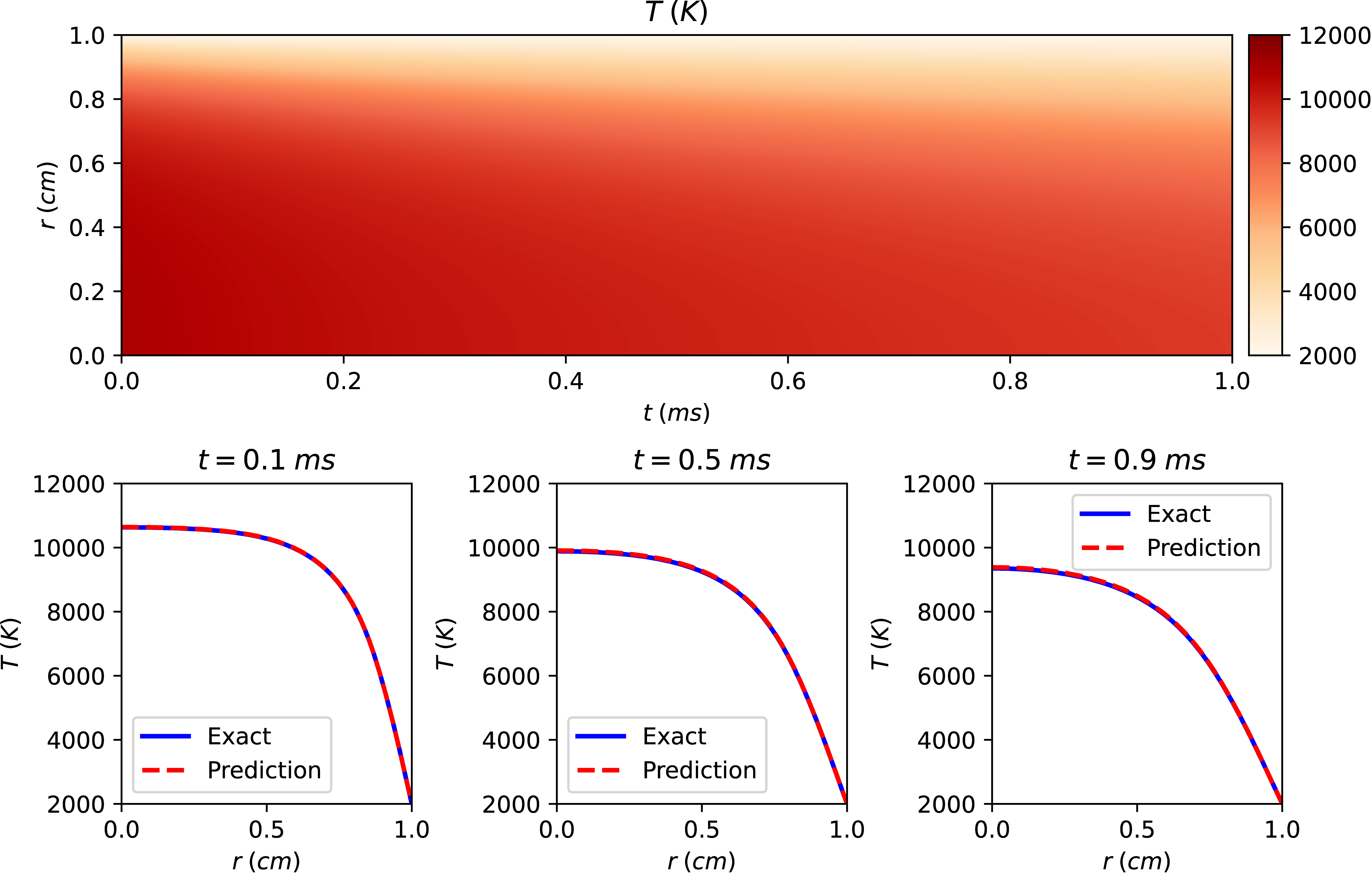
Spatial and temporal distribution of arc temperature in argon plasma at ambient pressure predicted by CS-PINN
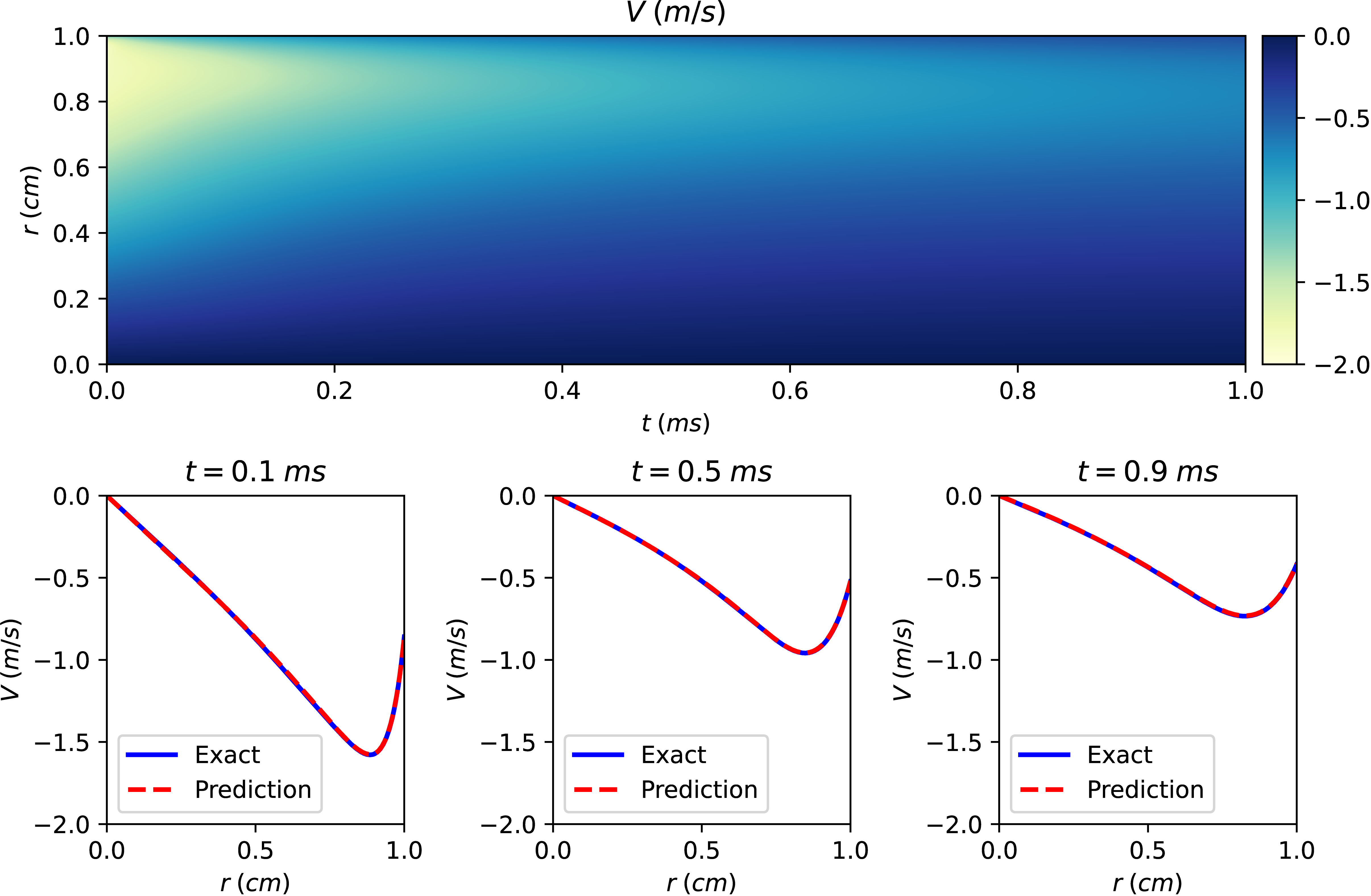
Spatial and temporal distribution of radial velocity in argon plasma at ambient pressure predicted by CS-PINN
Case 4: Solving time-dependent Elenbaas-Heller equation for 1-D arc plasma without initial condition
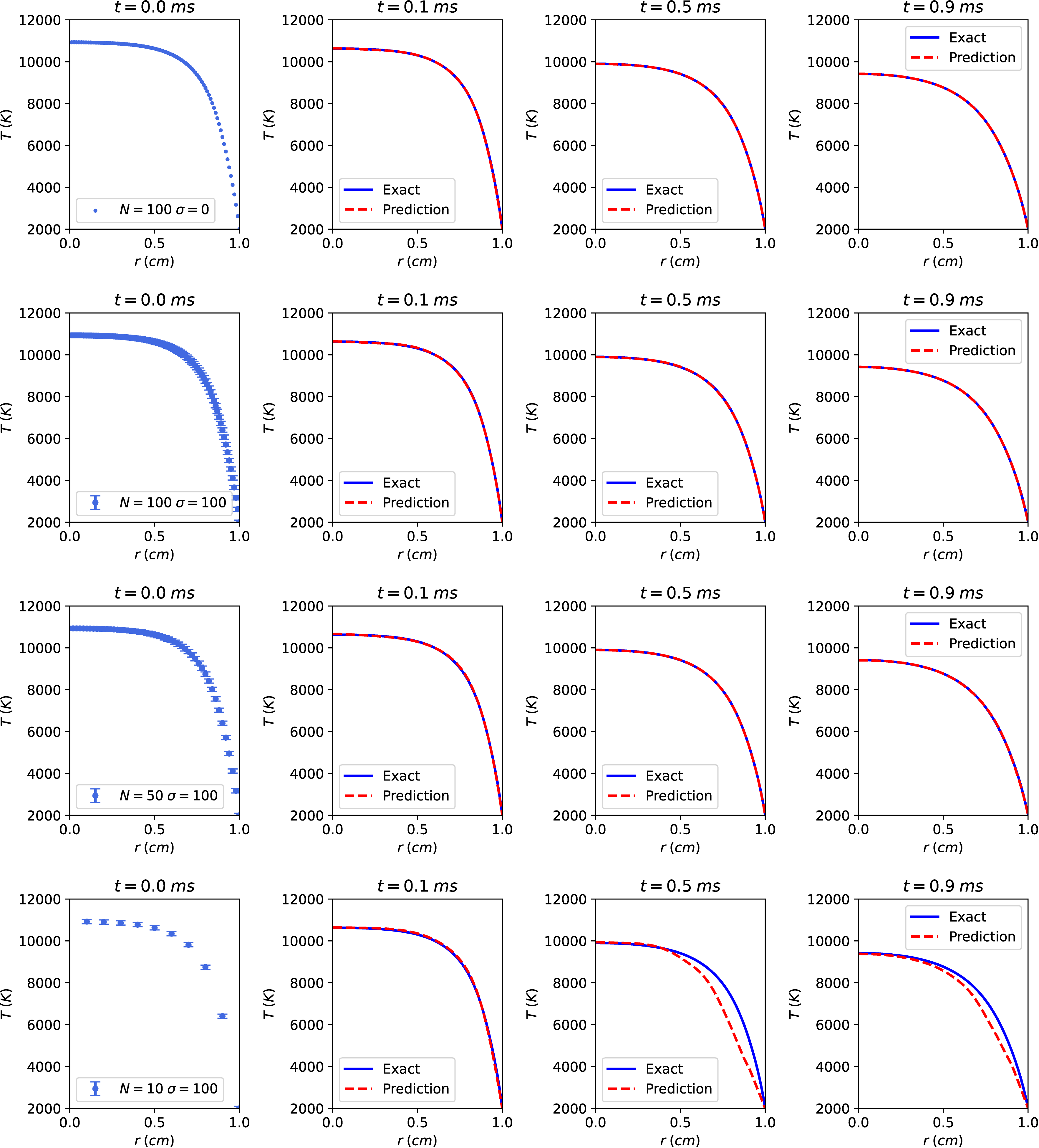
Spatial distribution of arc temperature in argon plasma at ambient pressure predicted by RK-PINN without an initial condition